Renewable Energy in Transport Saved 33.8 Mt CO2eq in 2012, up from 24.4 Mt CO2eq in 2009.
A new report by the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Union (EU), estimates that in 2012, when total GHG emissions reached the equivalent of 4546 Mt CO?, the deployment of all renewables in the EU avoided the equivalent of 716 Mt CO? emissions, or more than 15% of total emissions. The JRC report assesses data on the use of renewable energy, submitted by EU Member States every two years, and the latest report estimates that nearly two thirds of the total emissions savings in 2012 came from renewable energy development in Germany, Sweden, France, Italy and Spain.
According to the report, the highest contribution by renewables in 2012 came from renewable electricity, which accounted for the majority of the savings (64%), followed by renewable heating and cooling (31%) and renewable transport (5%). The 5% contribution in renewable transport is mostly made up of new technologies using biofuels, as well as electric vehicles receiving more of their power from solar/wind generation.
While the absolute contribution from renewables in the transport sector remained constant from 2009 to 2012, the proportion of GHG emission savings from renewables increased in the same period. This shows that although total emissions increased, the share of renewables in the sector also increased to match. This can be seen in the following table, which also shows an increase in emissions savings from renewables on a per capita basis.
|
Category of Emissions Savings |
2009 |
2012 |
|
Renewables as % of Total Savings |
5.3 |
5.3 |
|
Total Savings (Mt CO2eq) |
24.4 |
33.8 |
|
Per Capita Savings (kg CO2eq) |
50 |
70 |
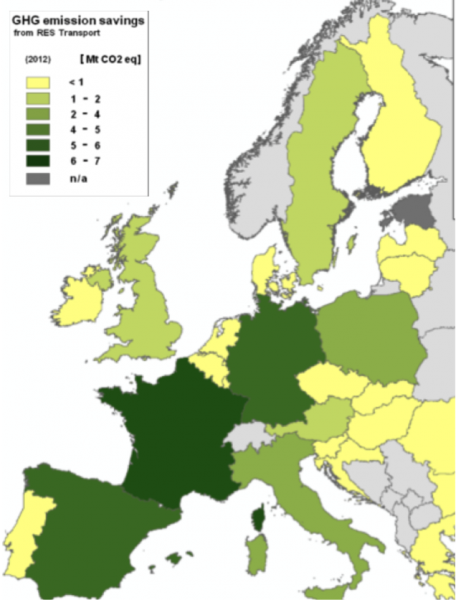
Of all the EU countries, France was the main GHG emissions saver due to the use of renewable energy in transport (6.16 Mt CO2eq), followed by Spain with 5.89 Mt CO2eq, Germany with 5.60 Mt CO2eq, Poland with 3.08 Mt CO2eq and Italy with 2.67 Mt CO2eq as can be seen in the graphic below.
It is essential to continue to increase the share of renewables in a sector that relies heavily on fossil fuels; a cleaner more sustainable transport sector is the way forward. With the consensus that developing nations will contribute the majority of transport emissions growth in the coming decades, it is hoped that the trend of increasing renewables in the EU foreshadows similar trends in the transport sector of developing nations.
The full report by the JRC, can be found here.
























